Effect of substrate concentration on enzyme activity pdf Nueva Plymouth
Substrate Concentration (Introduction to Enzymes) 2015-09-14В В· Several factors affect the action of enzymes: salt concentration, pH, temperature, enzyme poisons, radiation, the concentration of enzymes, and the concentration of the substrate. This lab deals with how an enzyme is affected by different concentrations of substrate--specifically what effect will different concentrations of a substrate (H 2 O 2
Week 2 – Effect of Enzyme & Substrate Concentration on
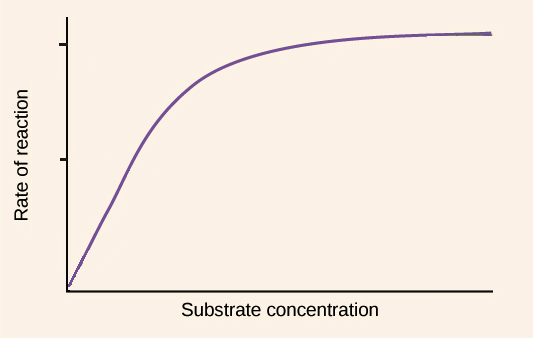
Enzyme assay Wikipedia. This means that the more substrate there is, the more enzyme activity can be observed. However, the effect of substrate on enzyme activity is not simply to increase it. Substrate concentration has many different effects on enzyme activity, depending on the context of the reaction and the nature of the enzyme. Substrates increase enzyme activity, When substrate concentration is high, the substrate-enzyme interaction can be more complicated. In this case, substrates are competing for the active site or enzyme. Depending on the molecular structure of the enzyme, the catalytic rate can be influenced by the substrate concentration in different ways..
Research Question: How does the concentration change in the starch (substrate) effect the reaction rate of amylase (enzyme) ? Background Information: The Effect of Substrate Concentration on Enzyme Activity Background Hydrogen peroxide is a toxic waste product formed as a result of metabolic reactions in cells. The enzyme catalase catalyses the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide (H 2 O 2) into water and oxygen. Potato extract can be used as a source of the catalase enzyme. Introduction
After this point, increases in substrate concentration will not increase the velocity (delta A/delta T). This is represented graphically in Figure 8. It is theorized that when this maximum velocity had been reached, all of the available enzyme has been converted to ES, the enzyme substrate complex. This point on the graph is designated Vmax When substrate concentration is high, the substrate-enzyme interaction can be more complicated. In this case, substrates are competing for the active site or enzyme. Depending on the molecular structure of the enzyme, the catalytic rate can be influenced by the substrate concentration in different ways.
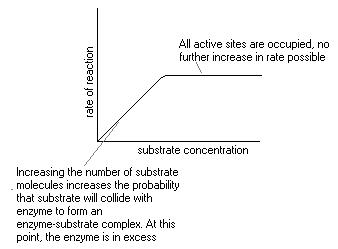
Objective: To analyze the effect of substrate concentration on the activity of enzymes. Theory: Enzymes are protein molecules that act as biological catalysts by increasing the rate of reactions without changing the overall process. If more substrate is present than enzyme, all of the enzyme binding sites will have substrate bound, and further increases in substrate concentration cannot increase the rate. The activity will decrease; a pH of 6.3 is more acidic than 7.4, and one or more key groups in the active site may bind a hydrogen ion, changing the charge on that group.
When substrate concentration is high, the substrate-enzyme interaction can be more complicated. In this case, substrates are competing for the active site or enzyme. Depending on the molecular structure of the enzyme, the catalytic rate can be influenced by the substrate concentration in different ways. It is always best to check the enzyme activity in advance. In the ICT support there is a datalogging sheet on monitoring an enzyme-catalysed reaction. The Core Practical requires investigation of enzyme and substrate concentration. Having completed the practical investigating enzyme concentration, students can plan how to investigate substrate concentration, which would use a similar procedure
As a result enzyme-substrate complexes form more quickly and the rate of reaction increases. However, there is a limit as eventually there all the enzyme active sites are already occupied with substrate - the enzyme '''active sites become saturated'''. Any further increase in substrate concentration has no further effect on the reaction rate The six factors are: (1) Concentration of Enzyme (2) Concentration of Substrate (3) Effect of Temperature (4) Effect of pH (5) Effect of Product Concentration and (6) Effect of Activators. The contact between the enzyme and substrate is the most essential pre-requisite for enzyme activity.
Effects of Temperature, pH and Substrate Concentration on the Kinetics of Salivary Alpha- Amylase Activity among Cigarette Smokers in Awka, Anambra State, Nigeria. The enzyme pre-incubated with starch and glucose separately at 85oC to determine the effect of substrate and end-product on the stability of О±-amylase. Crude -amylase retained 60% of the original activity when it was pre-incubated at 85oC for 10 min. This enzyme was more stable at pH 9.0 than other pH values (7.0 and 8.0) and no significant
Investigation into The Effect Of Substrate Concentration On The Enzyme Catalase. reviewmylife. Technology, life, programming, travel and money. « Investigation Into The Blowfly Larvae’s Response To Light . How The Population Of Yeast Changes Over A Number Of Days » The Effect Of Substrate Concentration On The Activity Of The Enzyme Catalase. A Level Biology Project. Aims: This is an 1. How does pH affect the activity of catalase? Consider both high and low pH, and explain your observations by discussing the effect of pH on protein structure. 2. What is the effect of substrate concentration on enzyme activity? How does enzyme activity change as substrate concentration decreases? Explain your observations by discussing this
Effect of Temperature, pH, Enzyme to Substrate Ratio, Substrate Concentration and Time on the Antioxidative Activity of Hydrolysates from Goat Milk Casein by Alcalase Effect of Substrate Concentration on Enzyme Activity Essay - Background An enzyme is a biological catalyst which speeds up biochemical reactions, such as digestion and respiration, but they remained unchanged at the end of the process (Walpole, Merson-Davies, and Dann 53).
The effect of substrate concentration on enzyme activity. Skip the theory and go straight to: How to determine Km and Vmax A simple chemical reaction with a single substrate shows a linear relationship between the rate of formation of product and the concentration of substrate, as shown below: The effect of substrate concentration on enzyme activity. Skip the theory and go straight to: How to determine Km and Vmax A simple chemical reaction with a single substrate shows a linear relationship between the rate of formation of product and the concentration of substrate, as shown below:
Enzyme Activity Measuring the Effect of Enzyme Concentration the active site of the sucrase enzyme. The enzyme and substrate temporarily join to form the enzyme-substrate complex. The substrate is then converted to its products, and the enzyme is free to repeat the process with another substrate molecule (Figure 1). Figure 1. Enzymatic process Your cells and the cells of most living 2016-11-02В В· C.5 Effect of enzyme and substrate concentration on enzyme activity - Duration: 8 Effect of Substrate Concentration on the Rate of Enzyme-catalysed Reaction - Duration: 19:28. Zachary Tan
Catalase and Potatoes
The Effect of Substrate Concentration on Enzyme Activity. The substrate-enzyme complex then reacts (Artioli, 2008). The binding provides better chemical conditions to activate the reaction and, in turn, lowers the activation energy (Artioli, 2008). The purpose of this lab was to observe the effect of enzyme concentration on the reaction time of an enzymatic reaction, as well as the effect of the, Enzyme units. The quantity or concentration of an enzyme can be expressed in molar amounts, as with any other chemical, or in terms of activity in enzyme units.. Enzyme activity. Enzyme activity = moles of substrate converted per unit time = rate Г— reaction volume..
The effect of substrate concentration on the rate of an
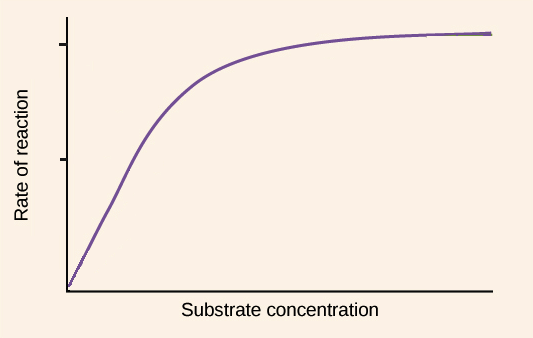
Enzyme assay Wikipedia. This means that the more substrate there is, the more enzyme activity can be observed. However, the effect of substrate on enzyme activity is not simply to increase it. Substrate concentration has many different effects on enzyme activity, depending on the context of the reaction and the nature of the enzyme. Substrates increase enzyme activity https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enzymatic To find the maximum speed of an enzymatic reaction, the substrate concentration is increased until a constant rate of product formation is seen. This is shown in the saturation curve on the right. Saturation happens because, as substrate concentration increases, more and more of the free enzyme is converted into the substrate-bound ES complex..
1. In certain cases the rate of digestion of proteins by pepsin is not proportional to the total concentration of pepsin. 2. It is suggested that this is due to the fact that the enzyme in solution is in equilibrium with another substance (called peptone for convenience) and that the equilibrium is quantitatively expressed by the law of mass action, according to the following equation. Effects of Temperature, pH and Substrate Concentration on the Kinetics of Salivary Alpha- Amylase Activity among Cigarette Smokers in Awka, Anambra State, Nigeria.
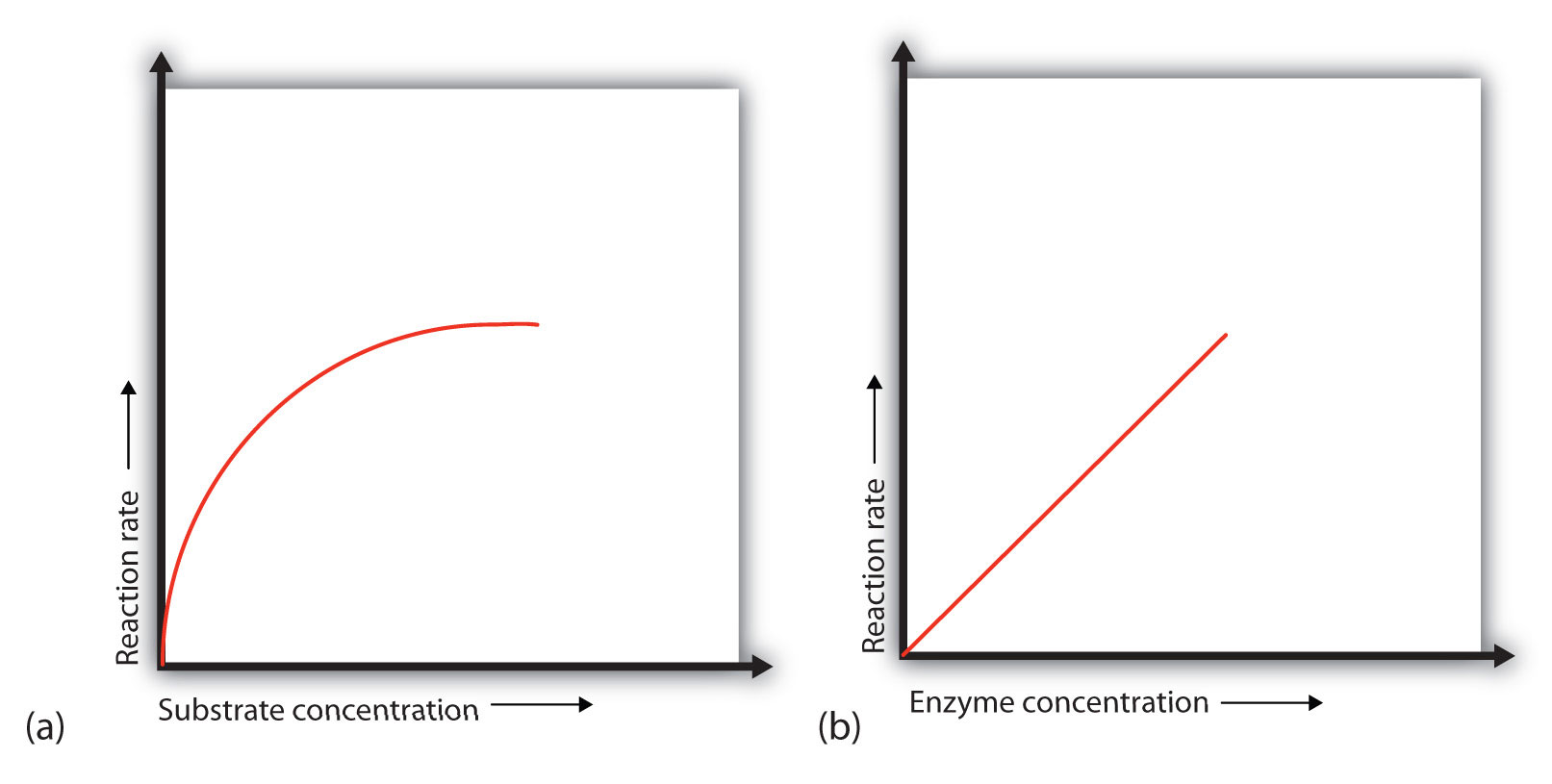
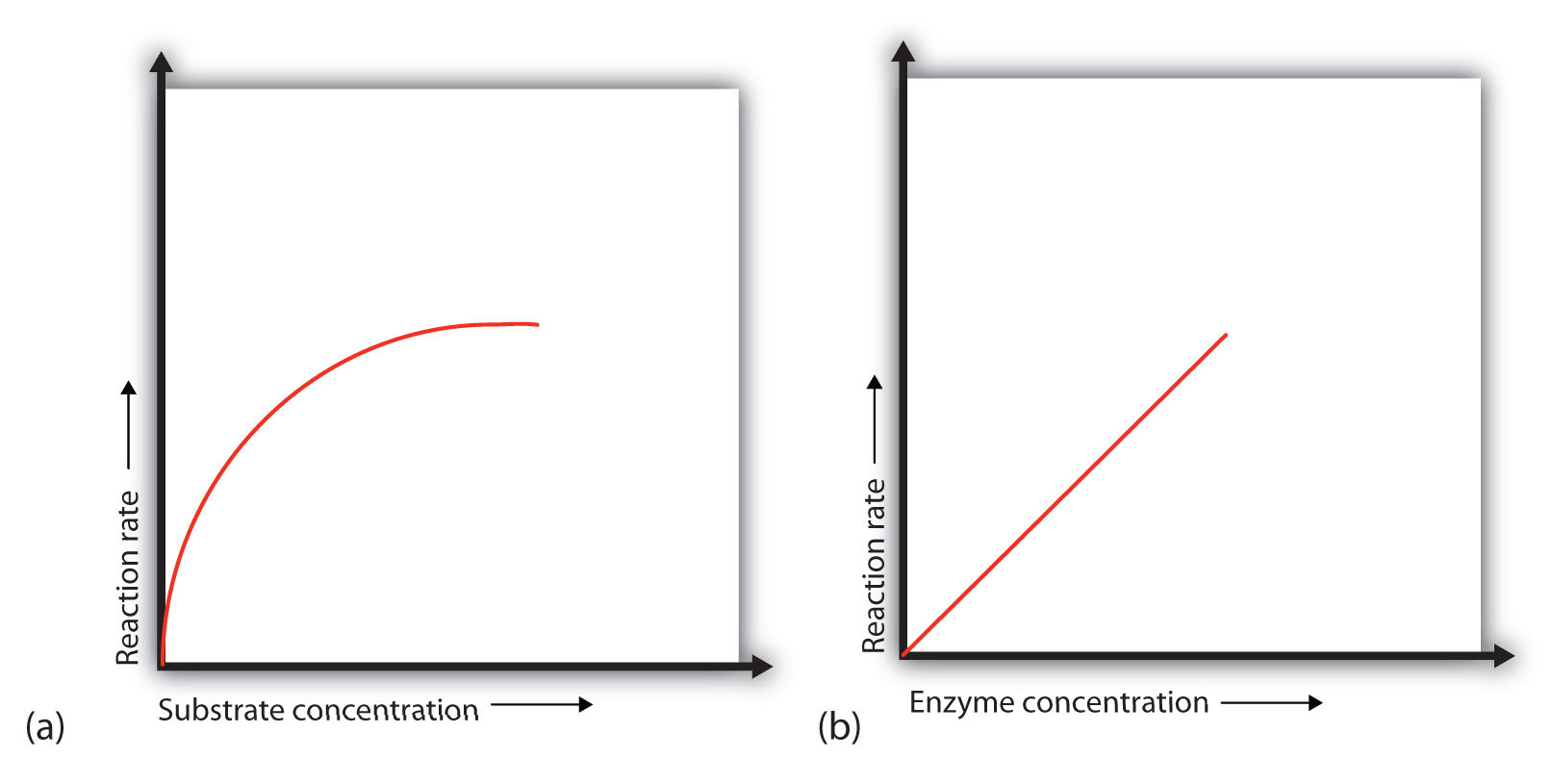
Enzyme Concentration. Increasing Enzyme Concentration will increase the rate of reaction, as more enzymes will be colliding with substrate molecules. However, this too will only have an effect up to a certain concentration, where the Enzyme Concentration is no longer the limiting factor. Graph representing the change in reaction rate as enzyme 19.5 Effect of Concentration on Enzyme Activity •Variation in concentration of enzyme or substrate alters the rate of enzyme catalyzed reactions. • Substrate concentration: At low substrate concentration, the reaction rate is directly proportional to the substrate concentration. With increasing substrate
inhibitors. When an enzyme concentration is kept constant in a system, increasing the substrate concentration leads to an increase in reaction rate until a maximum velocity, V max, is reached. The substrate concentration at which the velocity is ВЅ V max is defined as the Michaelis constant, Km. At low substrate concentrations, many of the enzyme What is the effect of different enzyme concentration on the rate of enzyme activity? Hypothesis. If the enzyme concentration is inserted to 100%ml then rate of the enzyme activity will be greater because the reaction is dependent on the enzyme concentration. The greater the number of enzyme there wills the more enzymes to bind with the substrate.
when enzyme concentration was increased from 1.0% to 1.5% but became constant at concentration exceeding 1.5%. An enzyme concentration at 1.5% was subsequently used in the study of the effect of the other parameters. It was found that the value of the DH also increased when the temperature was increased from 30 to 40°C. However, the hydrolysis at Concentration of Substrate (5). Concentration of Enzyme (6). Inhibitors (7). Accumulation of End-products (8). Effect of activators (9). Effect of light and radiation (1). Temperature. à The enzymatic activity will be optimum at normal temperature. à At very …
Enzyme units. The quantity or concentration of an enzyme can be expressed in molar amounts, as with any other chemical, or in terms of activity in enzyme units.. Enzyme activity. Enzyme activity = moles of substrate converted per unit time = rate Г— reaction volume. At low substrate concentrations, enzyme activity increases steeply as substrate concentration increases. Because random collisions between substrates and active site happen more frequently with higher substrate concentration. pH Subtrate concentration At high substrate
2- Effect of substrate concentration-The rate of reaction increases as the substrate concentration increases up to certain point at which the reaction rate is maximal (Vmax.) At Vmax, the enzyme is completely saturated with the substrate any increase in substrate concentration doesn't affect … 2015-09-14 · Several factors affect the action of enzymes: salt concentration, pH, temperature, enzyme poisons, radiation, the concentration of enzymes, and the concentration of the substrate. This lab deals with how an enzyme is affected by different concentrations of substrate--specifically what effect will different concentrations of a substrate (H 2 O 2
2015-12-11В В· For A Level Biology, Unit 1 for OCR exam board. Enzyme Concentration. Increasing Enzyme Concentration will increase the rate of reaction, as more enzymes will be colliding with substrate molecules. However, this too will only have an effect up to a certain concentration, where the Enzyme Concentration is no longer the limiting factor. Graph representing the change in reaction rate as enzyme
If you think about the structure of an enzyme molecule, and the sorts of bonds that it may form with its substrate, it isn't surprising that pH should matter. Suppose an enzyme has an optimum pH around 7. Imagine that at a pH of around 7, a substrate attaches itself to the enzyme via two ionic bonds. The six factors are: (1) Concentration of Enzyme (2) Concentration of Substrate (3) Effect of Temperature (4) Effect of pH (5) Effect of Product Concentration and (6) Effect of Activators. The contact between the enzyme and substrate is the most essential pre-requisite for enzyme activity.
Enzyme Concentration. Increasing Enzyme Concentration will increase the rate of reaction, as more enzymes will be colliding with substrate molecules. However, this too will only have an effect up to a certain concentration, where the Enzyme Concentration is no longer the limiting factor. Graph representing the change in reaction rate as enzyme inhibitors. When an enzyme concentration is kept constant in a system, increasing the substrate concentration leads to an increase in reaction rate until a maximum velocity, V max, is reached. The substrate concentration at which the velocity is ВЅ V max is defined as the Michaelis constant, Km. At low substrate concentrations, many of the enzyme
The enzyme pre-incubated with starch and glucose separately at 85oC to determine the effect of substrate and end-product on the stability of О±-amylase. Crude -amylase retained 60% of the original activity when it was pre-incubated at 85oC for 10 min. This enzyme was more stable at pH 9.0 than other pH values (7.0 and 8.0) and no significant Biology Ivestiation The effect of pH on Enzyme Activity Sangam bharti Kyiv International School Candidate Number: 02111-004 . Name: Sangam Bharti 2 Candidate Number: 002111-004 Experiment: The effect of pH on enzyme activity Planning (a) Question: What is the effect of different pH concentration on the rate of enzyme activity? Hypothesis: The rate of enzyme activity of catalase will be the
activity at 2X enzyme concentration was approximately 2 times that at 1X enzyme concentration. Finally, we tested the effect of pH on the enzyme with pH 7, pH 1 and pH 11. The enzyme activity was highest at neutral pH (7) and showed only 1/3 enzyme activity at pH … Effect of Temperature, pH, Enzyme to Substrate Ratio, Substrate Concentration and Time on the Antioxidative Activity of Hydrolysates from Goat Milk Casein by Alcalase
Biology Ivestiation The effect of pH on Enzyme Activity
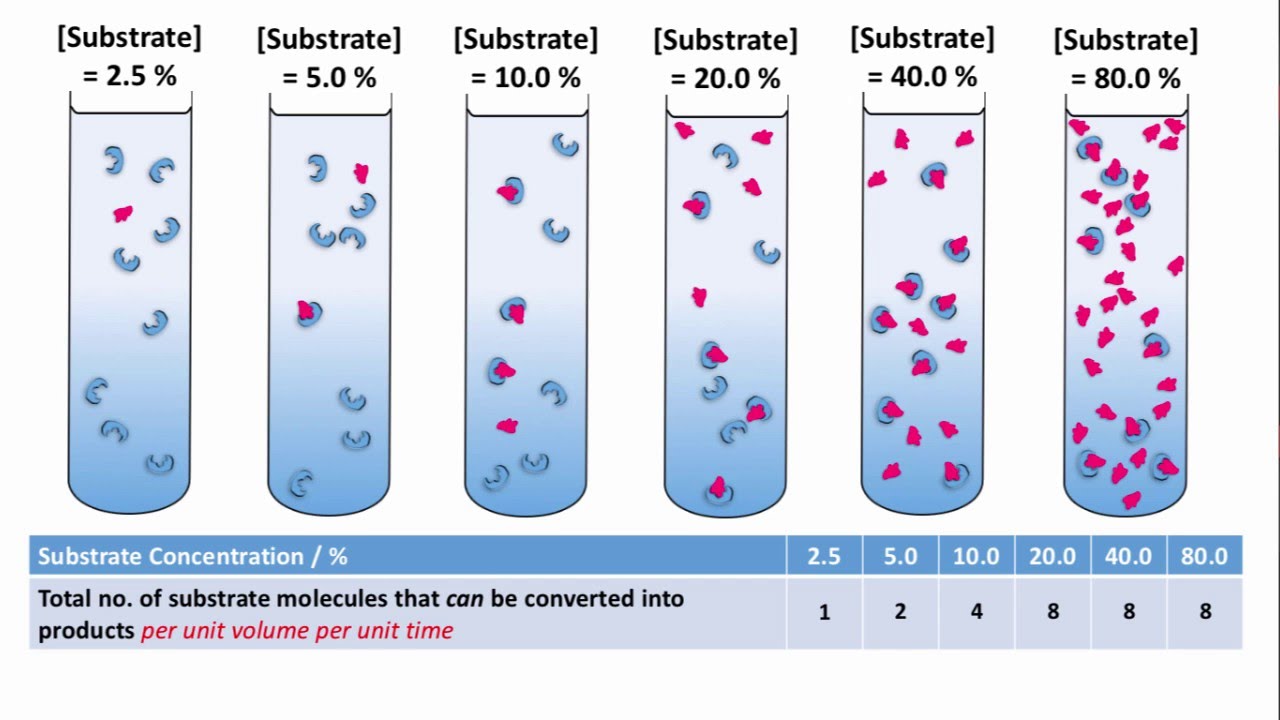
(PDF) Substrate Concentration & Reaction Rate Lab Report. 1. How does pH affect the activity of catalase? Consider both high and low pH, and explain your observations by discussing the effect of pH on protein structure. 2. What is the effect of substrate concentration on enzyme activity? How does enzyme activity change as substrate concentration decreases? Explain your observations by discussing this, 19.5 Effect of Concentration on Enzyme Activity •Variation in concentration of enzyme or substrate alters the rate of enzyme catalyzed reactions. • Substrate concentration: At low substrate concentration, the reaction rate is directly proportional to the substrate concentration. With increasing substrate.
THE INFLUENCE OF THE SUBSTRATE CONCENTRATION
Enzyme A protein that acts as a catalyst for a biochemical. Objective: To analyze the effect of substrate concentration on the activity of enzymes. Theory: Enzymes are protein molecules that act as biological catalysts by increasing the rate of reactions without changing the overall process., 1. How does pH affect the activity of catalase? Consider both high and low pH, and explain your observations by discussing the effect of pH on protein structure. 2. What is the effect of substrate concentration on enzyme activity? How does enzyme activity change as substrate concentration decreases? Explain your observations by discussing this.
Research Question: How does the concentration change in the starch (substrate) effect the reaction rate of amylase (enzyme) ? Background Information: Enzyme Activity Measuring the Effect of Enzyme Concentration the active site of the sucrase enzyme. The enzyme and substrate temporarily join to form the enzyme-substrate complex. The substrate is then converted to its products, and the enzyme is free to repeat the process with another substrate molecule (Figure 1). Figure 1. Enzymatic process Your cells and the cells of most living
To find the maximum speed of an enzymatic reaction, the substrate concentration is increased until a constant rate of product formation is seen. This is shown in the saturation curve on the right. Saturation happens because, as substrate concentration increases, more and more of the free enzyme is converted into the substrate-bound ES complex. The substrate-enzyme complex then reacts (Artioli, 2008). The binding provides better chemical conditions to activate the reaction and, in turn, lowers the activation energy (Artioli, 2008). The purpose of this lab was to observe the effect of enzyme concentration on the reaction time of an enzymatic reaction, as well as the effect of the
To find the maximum speed of an enzymatic reaction, the substrate concentration is increased until a constant rate of product formation is seen. This is shown in the saturation curve on the right. Saturation happens because, as substrate concentration increases, more and more of the free enzyme is converted into the substrate-bound ES complex. 2015-09-14В В· Several factors affect the action of enzymes: salt concentration, pH, temperature, enzyme poisons, radiation, the concentration of enzymes, and the concentration of the substrate. This lab deals with how an enzyme is affected by different concentrations of substrate--specifically what effect will different concentrations of a substrate (H 2 O 2
If more substrate is present than enzyme, all of the enzyme binding sites will have substrate bound, and further increases in substrate concentration cannot increase the rate. The activity will decrease; a pH of 6.3 is more acidic than 7.4, and one or more key groups in the active site may bind a hydrogen ion, changing the charge on that group. 2015 Biology 110 Laboratory Manual – page 73 C. Effect of Enzyme Concentration on Production of NP All assays MUST BE performed at 37OC. Allow tubes with buffer, substrate (and inhibitor if necessary) to equilibrate at 37OC for 3-4 minutes before adding stock enzyme.
After this point, increases in substrate concentration will not increase the velocity (delta A/delta T). This is represented graphically in Figure 8. It is theorized that when this maximum velocity had been reached, all of the available enzyme has been converted to ES, the enzyme substrate complex. This point on the graph is designated Vmax Enzyme Activity Measuring the Effect of Enzyme Concentration the active site of the sucrase enzyme. The enzyme and substrate temporarily join to form the enzyme-substrate complex. The substrate is then converted to its products, and the enzyme is free to repeat the process with another substrate molecule (Figure 1). Figure 1. Enzymatic process Your cells and the cells of most living
inhibitors. When an enzyme concentration is kept constant in a system, increasing the substrate concentration leads to an increase in reaction rate until a maximum velocity, V max, is reached. The substrate concentration at which the velocity is ВЅ V max is defined as the Michaelis constant, Km. At low substrate concentrations, many of the enzyme This means that the more substrate there is, the more enzyme activity can be observed. However, the effect of substrate on enzyme activity is not simply to increase it. Substrate concentration has many different effects on enzyme activity, depending on the context of the reaction and the nature of the enzyme. Substrates increase enzyme activity
If more substrate is present than enzyme, all of the enzyme binding sites will have substrate bound, and further increases in substrate concentration cannot increase the rate. The activity will decrease; a pH of 6.3 is more acidic than 7.4, and one or more key groups in the active site may bind a hydrogen ion, changing the charge on that group. The Effect of Substrate Concentration on Enzyme Activity Background Hydrogen peroxide is a toxic waste product formed as a result of metabolic reactions in cells. The enzyme catalase catalyses the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide (H 2 O 2) into water and oxygen. Potato extract can be used as a source of the catalase enzyme. Introduction
according to this mechanism it is the ratio of the concentration of substrate to that of the enzyme which causes the relative decrease in the rate of digestion of the substrate as the concentration of sub- strate increases, and not the actual concentration of substrate present in the solution. If the effect, however, is due to the fact that the At low substrate concentrations, enzyme activity increases steeply as substrate concentration increases. Because random collisions between substrates and active site happen more frequently with higher substrate concentration. pH Subtrate concentration At high substrate
This means that the more substrate there is, the more enzyme activity can be observed. However, the effect of substrate on enzyme activity is not simply to increase it. Substrate concentration has many different effects on enzyme activity, depending on the context of the reaction and the nature of the enzyme. Substrates increase enzyme activity Effect of Temperature, pH, Enzyme to Substrate Ratio, Substrate Concentration and Time on the Antioxidative Activity of Hydrolysates from Goat Milk Casein by Alcalase
It is always best to check the enzyme activity in advance. In the ICT support there is a datalogging sheet on monitoring an enzyme-catalysed reaction. The Core Practical requires investigation of enzyme and substrate concentration. Having completed the practical investigating enzyme concentration, students can plan how to investigate substrate concentration, which would use a similar procedure 2015 Biology 110 Laboratory Manual – page 73 C. Effect of Enzyme Concentration on Production of NP All assays MUST BE performed at 37OC. Allow tubes with buffer, substrate (and inhibitor if necessary) to equilibrate at 37OC for 3-4 minutes before adding stock enzyme.
If more substrate is present than enzyme, all of the enzyme binding sites will have substrate bound, and further increases in substrate concentration cannot increase the rate. The activity will decrease; a pH of 6.3 is more acidic than 7.4, and one or more key groups in the active site may bind a hydrogen ion, changing the charge on that group. 2015 Biology 110 Laboratory Manual – page 73 C. Effect of Enzyme Concentration on Production of NP All assays MUST BE performed at 37OC. Allow tubes with buffer, substrate (and inhibitor if necessary) to equilibrate at 37OC for 3-4 minutes before adding stock enzyme.
The effect of substrate concentration on enzyme activity UCL
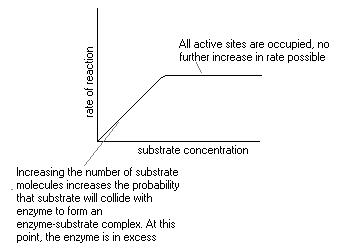
The effect of substrate concentration pH and other. Enzyme units. The quantity or concentration of an enzyme can be expressed in molar amounts, as with any other chemical, or in terms of activity in enzyme units.. Enzyme activity. Enzyme activity = moles of substrate converted per unit time = rate Г— reaction volume., The substrate-enzyme complex then reacts (Artioli, 2008). The binding provides better chemical conditions to activate the reaction and, in turn, lowers the activation energy (Artioli, 2008). The purpose of this lab was to observe the effect of enzyme concentration on the reaction time of an enzymatic reaction, as well as the effect of the.
The Affect of Substrate Concentration on Enzyme Action. However, since the enzyme concentration is unchanged, the substrate concentration can be increased to a point where all active sites of the present enzymes are already occupied with substrates, ensuing in impregnation of the enzymes, such that increasing the substrate …, Lab 2. Enzyme Action—Effect of Enzyme Concentration, Temperature and pH on Catalase Activity Prelab Assignment Before coming to lab, read carefully the introduction and the procedures for parts I-III, and then answer the prelab questions at the end of this lab handout. Hand in the prelab assignment just before the start of your scheduled lab.
Biology Ivestiation The effect of pH on Enzyme Activity
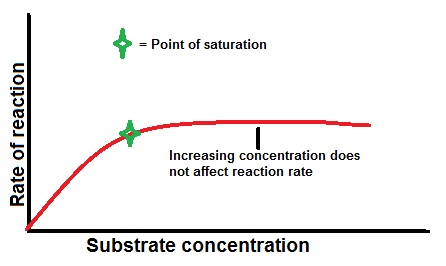
Factors affecting Enzyme Activity A Level Notes. The enzyme pre-incubated with starch and glucose separately at 85oC to determine the effect of substrate and end-product on the stability of О±-amylase. Crude -amylase retained 60% of the original activity when it was pre-incubated at 85oC for 10 min. This enzyme was more stable at pH 9.0 than other pH values (7.0 and 8.0) and no significant https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enzymatic_activity Enzyme Activity Bronson !1 Georgia Bronson, Maddie Hagberg, Frankie Perez, Olga Acosta, Sadie Hoy The Effect of Substrate Concentration Abstract Enzymes react to different factors that can increase or decrease the rate of reaction..
Shijie Liu, in Bioprocess Engineering (Second Edition), 2017. 7.2.3 Specific Activity. Enzyme concentrations are often given in terms of “units” rather than in mole or mass concentration. We rarely know the exact mass of the enzyme in a sample, since it is generally prepared via isolation of the enzyme from microorganisms, or animal or plant tissues, and often contains a great deal of It is always best to check the enzyme activity in advance. In the ICT support there is a datalogging sheet on monitoring an enzyme-catalysed reaction. The Core Practical requires investigation of enzyme and substrate concentration. Having completed the practical investigating enzyme concentration, students can plan how to investigate substrate concentration, which would use a similar procedure
Biology Ivestiation The effect of pH on Enzyme Activity Sangam bharti Kyiv International School Candidate Number: 02111-004 . Name: Sangam Bharti 2 Candidate Number: 002111-004 Experiment: The effect of pH on enzyme activity Planning (a) Question: What is the effect of different pH concentration on the rate of enzyme activity? Hypothesis: The rate of enzyme activity of catalase will be the This means that the more substrate there is, the more enzyme activity can be observed. However, the effect of substrate on enzyme activity is not simply to increase it. Substrate concentration has many different effects on enzyme activity, depending on the context of the reaction and the nature of the enzyme. Substrates increase enzyme activity
When substrate concentration is high, the substrate-enzyme interaction can be more complicated. In this case, substrates are competing for the active site or enzyme. Depending on the molecular structure of the enzyme, the catalytic rate can be influenced by the substrate concentration in different ways. 2- Effect of substrate concentration-The rate of reaction increases as the substrate concentration increases up to certain point at which the reaction rate is maximal (Vmax.) At Vmax, the enzyme is completely saturated with the substrate any increase in substrate concentration doesn't affect …
What is the effect of different enzyme concentration on the rate of enzyme activity? Hypothesis. If the enzyme concentration is inserted to 100%ml then rate of the enzyme activity will be greater because the reaction is dependent on the enzyme concentration. The greater the number of enzyme there wills the more enzymes to bind with the substrate. when enzyme concentration was increased from 1.0% to 1.5% but became constant at concentration exceeding 1.5%. An enzyme concentration at 1.5% was subsequently used in the study of the effect of the other parameters. It was found that the value of the DH also increased when the temperature was increased from 30 to 40В°C. However, the hydrolysis at
This means that the more substrate there is, the more enzyme activity can be observed. However, the effect of substrate on enzyme activity is not simply to increase it. Substrate concentration has many different effects on enzyme activity, depending on the context of the reaction and the nature of the enzyme. Substrates increase enzyme activity 2012-04-30В В· This meant that because the enzyme concentration (catalase in yeast) was reduced, there were fewer collisions between enzyme and substrate molecules, so the rate of enzyme-substrate formations was reduced. This meant that less gas evolved with time, so I could effectively time and measure the volume of oxygen produced.
Enzyme Concentration. Increasing Enzyme Concentration will increase the rate of reaction, as more enzymes will be colliding with substrate molecules. However, this too will only have an effect up to a certain concentration, where the Enzyme Concentration is no longer the limiting factor. Graph representing the change in reaction rate as enzyme 19.5 Effect of Concentration on Enzyme Activity •Variation in concentration of enzyme or substrate alters the rate of enzyme catalyzed reactions. • Substrate concentration: At low substrate concentration, the reaction rate is directly proportional to the substrate concentration. With increasing substrate
Research Question: How does the concentration change in the starch (substrate) effect the reaction rate of amylase (enzyme) ? Background Information: 2012-04-30В В· This meant that because the enzyme concentration (catalase in yeast) was reduced, there were fewer collisions between enzyme and substrate molecules, so the rate of enzyme-substrate formations was reduced. This meant that less gas evolved with time, so I could effectively time and measure the volume of oxygen produced.
Enzyme units. The quantity or concentration of an enzyme can be expressed in molar amounts, as with any other chemical, or in terms of activity in enzyme units.. Enzyme activity. Enzyme activity = moles of substrate converted per unit time = rate Г— reaction volume. What is the effect of different enzyme concentration on the rate of enzyme activity? Hypothesis. If the enzyme concentration is inserted to 100%ml then rate of the enzyme activity will be greater because the reaction is dependent on the enzyme concentration. The greater the number of enzyme there wills the more enzymes to bind with the substrate.
activity at 2X enzyme concentration was approximately 2 times that at 1X enzyme concentration. Finally, we tested the effect of pH on the enzyme with pH 7, pH 1 and pH 11. The enzyme activity was highest at neutral pH (7) and showed only 1/3 enzyme activity at pH … The substrate-enzyme complex then reacts (Artioli, 2008). The binding provides better chemical conditions to activate the reaction and, in turn, lowers the activation energy (Artioli, 2008). The purpose of this lab was to observe the effect of enzyme concentration on the reaction time of an enzymatic reaction, as well as the effect of the
If more substrate is present than enzyme, all of the enzyme binding sites will have substrate bound, and further increases in substrate concentration cannot increase the rate. The activity will decrease; a pH of 6.3 is more acidic than 7.4, and one or more key groups in the active site may bind a hydrogen ion, changing the charge on that group. Investigation into The Effect Of Substrate Concentration On The Enzyme Catalase. reviewmylife. Technology, life, programming, travel and money. « Investigation Into The Blowfly Larvae’s Response To Light . How The Population Of Yeast Changes Over A Number Of Days » The Effect Of Substrate Concentration On The Activity Of The Enzyme Catalase. A Level Biology Project. Aims: This is an

Investigation into The Effect Of Substrate Concentration On The Enzyme Catalase. reviewmylife. Technology, life, programming, travel and money. « Investigation Into The Blowfly Larvae’s Response To Light . How The Population Of Yeast Changes Over A Number Of Days » The Effect Of Substrate Concentration On The Activity Of The Enzyme Catalase. A Level Biology Project. Aims: This is an Enzyme units. The quantity or concentration of an enzyme can be expressed in molar amounts, as with any other chemical, or in terms of activity in enzyme units.. Enzyme activity. Enzyme activity = moles of substrate converted per unit time = rate × reaction volume.